Can You Charge A Lithium Battery With A Trickle Charger
The trickle charger is an essential tool for automotive maintenance and battery care. Understanding the operation and benefits of a trickle charger is critical for ensuring the longevity and performance of your battery, whether in a car, motorcycle, boat, or any other vehicle with a battery.
In this post, we'll look into trickle chargers, including their purpose, how they function, and why they're such an important tool for keeping your vehicle's battery in good working order.
Table of Content
- Part 1. Understanding the Trickle Charger
- Part 2. How Does a Trickle Charger Work?
- Part 3. When to Utilize a Trickle Charger
- Part 4. Can a Trickle Charger Fully Charge a Battery?
- Part 5. Differences Between Trickle Chargers and Battery Chargers
- Part 6. How to Properly Use a Trickle Charger
- Part 7. How Long Should a Trickle Charger Remain Connected to a Battery?
- Part 8. Drawbacks of Battery Trickle Chargers
- Part 9. Alternatives to Trickle Chargers
- Part 10. Can You Charge a Lithium Battery with a Trickle Charger
Part 1. Understanding the Trickle Charger
A trickle charger, also known as a float charger, is a device that delivers a low, steady current to a battery, keeping it charged and ready for use even after extended periods of inactivity. Unlike standard chargers, which give a large current to quickly charge a battery and then turn off, a trickle charger delivers a little amount of electricity continually. This slow and steady technique helps to combat the self-discharge that occurs in batteries over time, thereby keeping them charged without overcharging.
Part 2. How Does a Trickle Charger Work?
Trickle chargers have circuitry that regulates the flow of current to the battery. When the battery voltage falls below a particular threshold, the trickle charger turns on and begins giving a tiny, steady current to the battery. As the battery approaches full charge, the trickle charger decreases the current flow to prevent overcharging. This clever charging procedure helps to keep the battery charged without causing any damage due to overcharging.
Part 3. When to Utilize a Trickle Charger
A trickle charger is useful when you need to store batteries for an extended period of time. Whether you're keeping your car parked for a lengthy period of time, storing your RV throughout the winter, or trying to keep your boat batteries charged, there are various reasons to consider investing in one.
Additionally, the sort of batteries you have may influence your decision. Self-discharge rates differ among batteries. For example, lead-acid batteries normally self-discharge at a rate of 10-15% per month, whereas LiFePO4 batteries tend to degrade at a far slower pace. For example, Power Queen Batteries have a self-discharge rate of only 2-3% each month.

As a result, based on how long your batteries will be stored, the type of batteries you possess, and the level of safety measures you require, you may choose the best trickle charger for your purposes.
Part 4. Can a Trickle Charger Fully Charge a Battery?
A trickle charger can fully charge a battery; however, it will take a significant length of time. Trickle chargers typically output between 1 and 3 amps, thus a complete charge could take many days. For example, a 1-amp trickle charger will take around 100 hours to fully charge a drained 100Ah battery. This method is noticeably wasteful, as trickle chargers' principal function is to keep your batteries charged.
If your batteries are entirely depleted or have a low charge, it is strongly advised to use a standard battery charger to quickly recharge them. While lead-acid batteries can take up to 8 hours to fully charge, a 100Ah Power Queen lithium battery should take only two to three hours to charge with the proper charger.
Part 5. Differences Between Trickle Chargers and Battery Chargers
Trickle chargers and battery chargers serve varied functions and operate in different ways, catering to unique battery maintenance and charging requirements. Understanding the distinctions between these two gadgets is critical for selecting the best tool for your needs. To further understand their functions and uses, we'll look at the differences between trickle chargers and battery chargers.
5.1 Trickle Chargers
Purpose: Trickle chargers are intended to supply a low, steady current to a battery, allowing it to retain its charge during long periods of inactivity or storage. Their principal role is to counteract the natural self-discharge of a battery and keep it from depleting altogether.
Charging Method: Trickle chargers provide a tiny, constant current to the battery, ensuring that it maintains an appropriate charge without overcharging. They are meant to be left connected to the battery for extended periods of time without causing damage to the battery.
Long-Term Maintenance: Ideal for long-term storage of vehicles such as antique cars, motorbikes, boats, and seasonal vehicles, since they help to maintain the battery's charge and prevent complications caused by inactivity.
Prevention of Sulfation: Trickle chargers aid to reduce sulfation, a common cause of battery failure, by maintaining a steady charge and preventing the production of lead sulfate crystals on the battery plates.
5.2 Battery Chargers
Purpose: Battery chargers are designed to fast recharge a depleted battery by delivering a high current until the battery is fully charged. They are frequently used to recharge a dead or substantially drained battery.
Charging Method: Battery chargers, as opposed to trickle chargers, give a larger current to the battery, allowing for faster charging. Most current battery chargers have automated shut-off mechanisms that prevent overcharging once the battery is fully charged.
Emergency Charging: Battery chargers are frequently utilized in emergency scenarios where a vehicle's battery has been fully depleted and must be recharged quickly to restore operation.
Maintenance Mode: Some current battery chargers also incorporate maintenance or trickle charge modes, which allow them to act similarly to trickle chargers for long-term battery maintenance once the initial charging procedure is over.

Part 6. How to Properly Use a Trickle Charger
Trickle chargers are intended to precisely regulate the charging process, preventing overcharging and keeping the battery at full capacity by charging at a pace comparable to the battery's self-discharge rate. Rapid charging or overcharging can cause battery damage.
The technique of using a trickle charger is basic. Most trickle chargers are made up of a small box containing the charger's components, a power line, and two alligator clips. Before making any connections, it is critical to determine the voltage and amperage levels appropriate for your battery. Before connecting the charger to a power source, make any necessary adjustments to the switches and buttons on the charger box.
6.1 Ensuring Battery Readiness
Before connecting the charger, follow the appropriate precautions. Park the vehicle in a well-ventilated, rain-free spot. Charging can produce surplus hydrogen gas, which, if concentrated in an enclosed location, might result in a fire or explosion. Ensure that the ignition is switched off, the key is removed, and the charger is unplugged.
6.2 Locating a Suitable Ground Point
Choosing a proper position to attach your charger's negative terminal is critical for the safe and effective completion of the trickle charger circuit. Ideally, utilize a bare metal location on the frame or a large bolt connecting to the chassis or engine block. If these are not available, a portion of the frame free of excessive filth, dust, and oil will do. Never utilize the battery's negative terminal, as this might cause a fire or an explosion.
6.3 Attaching Cables
Connect the alligator clips, which are normally black and red. Connect the red (positive) cable to the positive terminal of the battery to be charged. Once the secure connection has been established, connect the black (negative) wire to the ground point described in the previous step. Before you plug in the charger, make sure the negative wire is securely attached. To avoid significant shock or damage, do not touch the charger's cables while it is connected in and switched on.
Once all connections are secure, connect the trickle charger to a power outlet.
6.4 Activating the Charger
After connecting the necessary connections, make sure that all settings are set according to the manual's recommendations for the battery type being charged. Plug in the charger and turn it "On". Most battery chargers have an amp meter that reads higher for a dead battery and down to zero for a fully charged one. If the meter reads low, the battery may not require a charge, or the ground connection may be insufficient. In this instance, switch off the charger, unplug it, and try again.
Part 7. How Long Should a Trickle Charger Remain Connected to a Battery?
Most trickle chargers are designed to stay connected to your batteries for an extended amount of time. They are specifically designed to keep batteries charged even after months of storage. These gadgets assure battery owners that their batteries will be completely functional when they are ready to be retrieved and used again.
However, not all trickle chargers are made equally. If you like the "set it and forget it" method, a "automatic" or "smart" trickle charger may be the best option. These devices often include extra safety features, such as the ability to automatically limit the amperage they generate as the battery nears full charge. This ensures that your batteries remain fully charged without the risk of overcharging.
Part 8. Drawbacks of Battery Trickle Chargers
While trickle chargers can be effective, they are not foolproof and, like all chargers, must be monitored. They carry the same risks as their quicker equivalents, such as overheating and overcharging the battery if not used properly. In some situations, they may fail to charge fully dead batteries. Typically, investing in a trickle charger ahead of time is recommended to avoid reaching that level. Otherwise, leaving a trickle charger on a lawnmower during the winter may result in an unpleasant surprise in the spring, requiring the purchase of a new mower battery.
Issues can also arise from the type of battery utilized. If lead batteries are allowed to lose their charge, they might be damaged or rendered worthless. While most current trickle chargers have safety mechanisms to avoid overheating and overcharging, some may lack these safeguards. If a trickle charger fails to cut off, leaving it attached for an extended period of time can damage the battery. The essential message is to always make sure your charger has overload protection and voltage regulation.
Part 9. Alternatives to Trickle Chargers
When shopping for a new battery, keep in mind that lead-acid batteries are not the only option. Lithium batteries provide various advantages over lead-acid and other battery types, including a longer lifespan, higher charge capacity, and increased safety. In fact, LiFePO4 batteries reduce the need for a trickle charger in several ways. If you wish to continue using lead-acid batteries, Power Queen smart lithium battery chargers will immediately pause charging to prevent overcharging before changing to a trickle charge to sustain the battery.
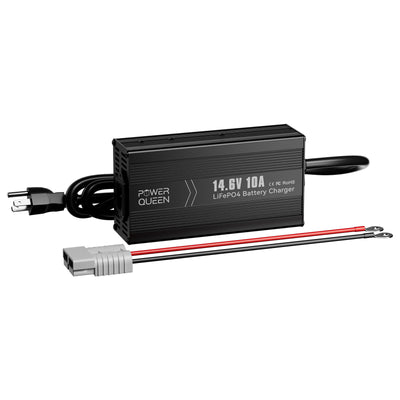


With a battery like the Power Queen 12V 100Ah Group 24 Smart lithium battery, which has Bluetooth technology, you can constantly monitor the charge state of your battery, preventing overcharging, which can be harmful to battery health.
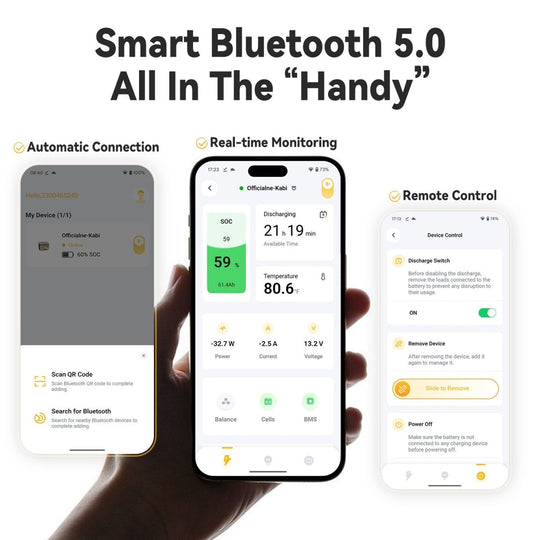
Furthermore, if your battery becomes empty, it may be safely recharged without creating a risk or becoming unusable. The built-in Battery Management System (BMS) helps to avoid damage by detecting adverse charging conditions, such as excessive temperatures, and stopping the charging process accordingly. These features reduce the guesswork involved in charging your battery.
Furthermore, the previously noted issue of sulfation does not apply to lithium batteries, which can handle a wider range of state-of-charge circumstances than lead batteries.
LiFePO4 lithium batteries come in a variety of sizes and are suitable for a wide range of applications, including trolling motors, RVs, and golf carts. Because of its smaller weight, faster charging capability, prolonged lifetime, and much longer lifespan, lithium batteries are known to be more efficient.
Part 10. Can You Charge a Lithium Battery with a Trickle Charger
Trickle charging is not appropriate for lithium batteries. Charging a LiFePO4 battery with a trickle charger that is not built for this type of battery may result in overcharging or damage due to the differences in charging needs between lithium batteries and standard lead acid batteries.
As a result, it is critical to use the right charger when charging a lithium battery. For further information, see How to Charge LiFePO4 Batteries.




























































